JPSC Syllabus & Exam Pattern
The JPSC Syllabus for the Combined Civil Service Exam is set by the Jharkhand Public Service Commission. The commission is authorized by the Constitution to assist the Jharkhand State Government in matters of recruitment, transfer, and disciplinary matters.
Recently the commission has released the JPSC notification. The JPSC 2024 exam notification and dates are not out yet. It is expected to be out shortly. We have given the JPSC syllabus and other details of the JPSC exam here.
The JPSC Exam Pattern for the Combined Civil Service Exam comprises 3 stages:
- Prelims – 2 Objective type papers for 200 Marks each.
- Mains – 6 Descriptive type Papers, all the papers are compulsory
- Personality Test – 100 Marks
JPSC 6 final result was announced on 21st April 2020.
Get JPSC 2024 details in the linked article.
JPSC Syllabus is very much aligned with the UPSC Syllabus. There would be a few minor differences, JPSC would concentrate more on the History and Geography of Jharkhand.
Candidates can check the JPSC eligibility in the linked article.
As per the notification released on 8th February 2021, the JPSC Syllabus and Exam pattern are given below in detail:
JPSC Exam Pattern for Prelims
The JPSC Prelims Exam consists of 2 compulsory papers.
JPSC Exam Pattern for Prelims is given in the below table:
Combined Civil Service Exam
Jharkhand Public Service Commission (JPSC)
2 papers on General Studies
2 Hours
200 Marks
400 Marks
JPSC Syllabus for Prelims
- History of India
- Geography of India
- Indian Polity and Governance
- Economic and Sustainable development
- Science and Technology
- Jharkhand-specific questions (General Awareness of its history, society, culture, and heritage)
- National and international current events
- General questions of miscellaneous nature
Find below the official notification on JPSC Syllabus for Prelims- General Studies – Paper 1


Find below the official notification on JPSC Syllabus for Prelims- General Studies – Paper 2

JPSC Exam Pattern for Mains
Candidates who have successfully cleared the Prelims stage will be eligible for JPSC Mains. Under usual circumstances, the number of candidates selected for Mains will be equal to 10 times the total number of vacancies.
The JPSC Exam pattern for Mains is given in the below table:
Combined Competitive Exam (Mains)
Jharkhand Public Service Commission (JPSC)
6 papers
3 hours each
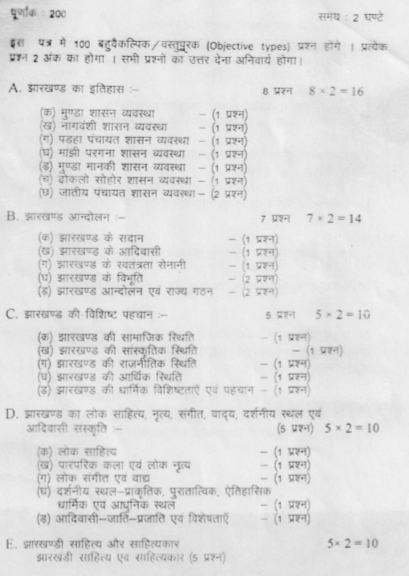
JPSC Syllabus for Mains
There are no optional papers in the JPSC Mains Syllabus. Also, marks of Paper-I will not be counted in the final merit list.
The details of the JPSC Syllabus for Mains are given below:
- Paper I: General Hindi and General English (100 Marks)
- Paper-II: Language and Literature (150 Marks)
- Paper III: Social Sciences, History and Geography (200 Marks)
- Paper IV: Indian Constitution, Polity, Public Administration and Good Governance (200 Marks)
- Paper V: Indian Economy, Globalization, and Sustainable Development (200 Marks)
- Paper VI: General Sciences, Environment & Technology Development (200 Marks)
JPSC Mains Syllabus – Paper 1 (General Hindi and General English)
This is just a qualifying paper. Out of 100 marks, every candidate will have to secure only 30 marks. Hence, the commission has made sure that candidates having an educational background in regional language will not be adversely impacted by the English section in the paper.
As per the JPSC exam pattern, Mains Paper 1 will have 2 sections:
- Hindi
- English
Both the sections will have equal weightage i.e. 50 marks each. The purpose of the paper is to test the working knowledge of the candidates in the above 2 languages. The level of both sections will be of metric standards.
As per the JPSC exam pattern, the paper will broadly test the candidate on the following:
- Essay
- Grammar
- Comprehension
- Precis
JPSC Mains Syllabus – Paper 2 (Language and Literature)
Candidates have to choose from one of the following languages and literature:
- Oriya Language and Literature
- Bengali Language and Literature
- Urdu Language and Literature
- Sanskrit Language and Literature
- English Language and Literature
- Hindi Language and Literature
- Santhali Language and Literature
- Panchpargania Language and Literature
- Nagpuri Language and Literature
- Mundari Language and Literature
- Kurux Language and Literature
- Kurmali Language and Literature
- Khortha Language and Literature
- Khadia Language and Literature
- Ho Language and Literature
JPSC Mains Syllabus – Paper 3 (Social Sciences, History and Geography)
As given in the JPSC exam pattern, Mains Paper 3 has 2 sections
- History
- Geography
The history section covers the syllabus from the following topics:
- Ancient period
- Medieval Period
- Modern Period
- History of Jharkhand
The geography section covers the syllabus from the following topics:
- Physical Geography (General Principles)
- Physical and Human Geography of India
- Natural Resources of India: Development and Utilization
- Geography of Jharkhand and utilization of its resources.
- Population
- Industrial and Urban Development
- The pattern of Urban Settlement and Pollution problems.
JPSC Mains Syllabus – Paper 4 (Indian Constitution, Polity, Public Administration and Good Governance)
As per the JPSC Mains Syllabus, candidates will have to handle topics from 2 sections in this Paper.
- Indian Constitution and Polity
- Public Administration and Good Governance
Indian Constitution and Polity covers the following topics
- Preamble, salient features of the Indian constitution, Fundamental Rights and Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy
- Union Government (Executive and Legislature)
- Judiciary
- State Government (Executive, Legislature, Judiciary, Panchayats and Municipalities)
- Centre-state relations
- Special provisions relating to the administration of Scheduled Areas and Scheduled Tribal Areas.
- Emergency provisions of the Constitution
- Election Commission of India
- Political parties and pressure groups
Public Administration and Good Governance covers the following topics
- Public Administration – Meaning, scope, and significance
- Public and private administration
- Union Administration – Central Secretariat, Cabinet Secretariat, Prime Ministers Office, Planning Commission, Finance Commission
- State Administration- State Secretariat, Chief Secretary, Chief Minister Office
- District Administration – Origin and development of the office of District Magistrate and Collector, the changing role of the District Collector, the impact of the separation of the judiciary on district administration
- Personnel Administration – Recruitment of civil services, Union Public Service Commission and State Public Service Commission, training of civil servants, leadership and its qualities, employees morale and productivity
- Delegation, Centralization, and decentralization of authority
- Bureaucracy – its merits and demerits, the role of bureaucracy in policy formulation and its implementation; nexus between bureaucracy and political executive; generalist versus specialist
- Development Administration
- Disaster Management- causes, mitigation, classification of disasters, immediate and long-term measures
- Good governance – Lokpal, Lokayukta, Central Vigilance Commissioner, grievance redressal, right to service act, right to information act, right to education act, consumer protection act, domestic violence against women (prevention) act
- Human Rights – concept, meaning, universal declaration of human rights, National Human Rights Commission, State Human Rights Commission, terrorism, social issues
JPSC Mains Syllabus – Paper 5 (Indian Economy, Globalization, and Sustainable Development)
Paper 5 is based on the Indian Economy, Globalization, and Sustainable Development. The JPSC Mains Syllabus for Paper Five is given below:
Basic Features of the Indian Economy
- National Income – elementary concepts of national income, and methods of its calculation, for example – GDP, GNP, NDP, NNP, GSDP, NSDP, DDP at constant and current prices, at factor cost, etc
- Inflation – Concept, control of inflation, monetary, fiscal, and direct measures.
- Demographic features
- Agriculture and Rural economy – green revolution, white revolution, rainbow revolution, WTO
- Industrial economy – policy initiative and changes
- Public finance – the scope of public finance, principles of public finance, taxation
- Public expenditure
- Budget
- Fiscal policy- center and state fiscal relationship, the role of the finance commission
- Structure of Indian monetary and banking system in India.
- Indian Trade, Balance of Payment
Sustainable Development, Economic Issues, and Indian Development Strategy
- Meaning and measurement of Economic development; characteristics of underdevelopment, indicators of development: HDI, GDI, India’s HDI progress.
- Role of Foreign capital and technology in the growth of the economy
- Sustainable development – concept and indicators of sustainable development, economic, social and environmental sustainability, the concept of GDP
- Development status and issues about socially and economically marginalized sections, like ST, SC, religious minorities, schemes launched by the Central/State Government.
- Poverty and Unemployment: Measurements and trends, identification of BPL families, Multidimensional poverty index.
- Food and nutritional security – trends in food production and consumption in India, the problem of food security, problems and issues of storage, procurement, distribution, import, and export. Government policies, schemes, and programs such as the Public Distribution System, Mid-day meal schemes, government policies for food and nutritional security.
Economic Reforms, Nature and Impact on the Indian Economy
- New economic reforms – Liberalization, Privatisation, Globalization, a good understanding of International Finance Institutions like IMF, World Bank; and World Trade Organisation
- Financial and Banking sector reforms, economic reforms, NABARD, RRB
- Globalization of the Indian Economy – its positive and negative impacts on different sectors, issues of FDI and FII in India.
- Agriculture sector – Growth, Issues of subsidies, and public investment in agriculture
- Industrial development and economic reforms in India – major changes in Industrial policy, its impact on industrial growth, the role of public sector enterprises in India’s industrialization in post reforms period, disinvestment and privatization of public enterprises.
The economy of Jharkhand – features, issues, challenges, strategies
- Economic growth and structure of Jharkhand’s economy, sectoral composition, growth in SDP, and per capita NSDP in last decade, agricultural and industrial growth in Jharkhand.
- Demographic features of Jharkhand – population, growth, sex ratio, density, literacy, the composition of the workforce, rural-urban composition, etc.
- Status of poverty, unemployment, food security, malnutrition, education, and health indicators in Jharkhand, major initiatives, issues of agricultural and rural development, major programs and schemes, poverty alleviation programs, and food security schemes.
- Land, forest, and environmental issues in Jharkhand
JPSC Mains Syllabus – Paper 6 (General Sciences, Environment & Technology Development)
Candidates will have to handle topics from the following 5 sections.
- Physical Science
- Life Science
- Agriculture Science
- Environmental Science
- Science and Technology Development
Physical Science:
- Basic knowledge of the system of units like MKS, CGS, SI
- Topics on Speed, velocity, gravity, mass, weight, force, impact, work, power and energy
- Covers topics related to the solar system
- Concepts concerning sound, wavelength frequency, infrasonic and ultrasonic sound characteristics, and applications.
Life Science:
- Concepts on the living world, cell structure, its functions, diversity of organisms, biomolecules cell reproduction
- Medallion inheritance, theories of the evolution of life on earth, including human evolution.
Agriculture Science:
- A good understanding of the agro-climatic conditions of Jharkhand, rainfall patterns, and abiotic stresses in each zone.
- Knowledge of Food and horticultural crops of Jharkhand, understanding the need behind the diversification of crops, nutritional security due to the onset of climate change, the role of rainwater harvesting in improving agricultural production, and fish farming.
- Candidates are required to have sound knowledge of Soil fertility, measures that are undertaken to improve soil health, concepts on organic farming,agro-forestry, wastelands, and, government schemes to help the farmers of the state.
Environmental Science
- Measures that were taken by the Government of India to preserve the environment to tackle global environmental issues, air pollution, and water pollution.
- Understanding of numerous environmental laws.
- Candidates’ knowledge of Biodiversity hotspots and threats to biodiversity hotspots.
Science and Technology
- Indian Government policies concerning Nuclear technology, focus on global nuclear policies.
